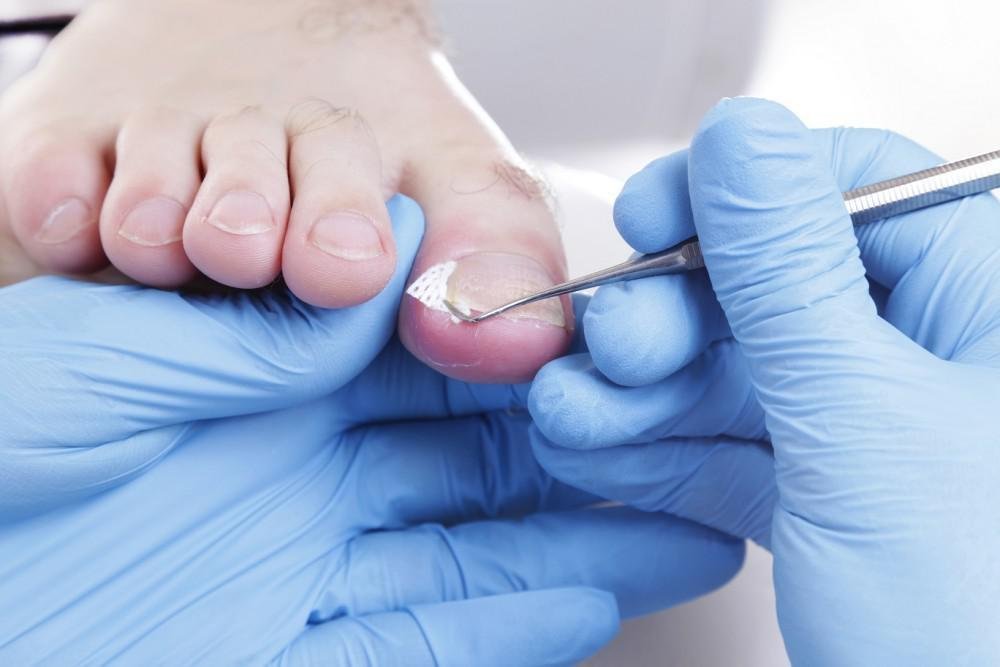
ingrown toenail
An ingrown toenail happens when a toenail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain and possibly infection.
Risk Factors:
Several factors may increase the risk of developing ingrown toenail including: incorrect nail trimming, tight shoes, toe injury, poor foot hygiene, genetic factors, fungal infections.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms include: pain and tenderness around the nail, redness and swelling, infection signs (more severe cases).
Diagnosis:
Ingrown toenail is typically diagnosed based on an examination of the toe and tests for infection.
Prevention:
To prevent ingrown toenail or reduce the risk of recurrence, you can: trim nails straight across, not too short, choose proper-fitting shoes, and keep feet clean and dry.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for ingrown toenail may include: foot soaks in warm water, lifting the nail gently, antibiotics for infection, nail removal (partial or full) for severe cases. If you have a persistent ingrown toenail that is causing you pain or discomfort, make an appointment with Dr. Aaron Bradley today.
-
Try soaking and lifting the nail. If pain continues, see a podiatrist.
-
Some may improve with proper care, but others may need medical treatment. If you have persistent symptoms that are causing you discomfort or pain, our team at Sole Foot & Ankle are ready to help.
-
Trim nails correctly and wear shoes that fit well.
-
No, minor cases may be treated without surgery but persistent or severe cases may require surgery.
-
Yes, especially if you have diabetes or circulation issues, they can lead to complications.
